Bengaluru Master plan: Will RMP 2035 meet the fate of RMP 2015?
Kathyayini Chamaraj for Bengaluru Citizen Matters • July 5, 2012
Citizens who participated in a discussion organised by CIVIC Bangalore today vehemently called for an effective mechanism for proper implementation of the Master Plan of BDA. The discussion was held in the light of BDA calling for inputs from citizens to its proposed Revised Master Plan (RMP) for 2035.

P S S Thomas, retired IAS officer and former chairman of the Advisory Committee on RMP 2015, who made the opening remarks, stressed the need for citizens to be involved at all stages of the planning process and not merely at the final draft stage. All 30 sister organisations, such as BWSSB, BESCOM, BMTC, etc., also needed to be involved in the consultation process, which had not happened during the drafting of RMP 2015.
There was no Action Taken Report on BDA’s website on RMP 2015 and no analysis of what challenges were faced and how they were met during its implementation except for the cryptic statement that "challenges were experienced during the implementation". The Advisory Committee had recommended that there should be a committee headed by the Chief Secretary to review the implementation of RMP 2015 but this had not been set up.
As such there was no institutional arrangement to monitor implementation of the Master Plan. Thomas also emphasised the need for civil society organisations to strengthen their own capacities for responding to the plans and for BDA to take ownership of the Plan and its implementation. He lamented the lack of an attempt at growth with equity in the plans.
Anjali Mohan, Consulting Urban and Regional Planner, emphasised the need for building in the process of involving citizens and other line agencies of the government at every stage of the planning while submitting the Request for Proposal itself to the consultants.
The necessary finances and time-frames too for this process needed to be built into the bid. Though training and capacity building of BDA had been undertaken during the roll out process of RMP 2015, it did not bring in ownership of the Plan and its implementation by BDA. It was essential to ensure that RMP 2035 did not meet the same fate. She also lamented the lack of consonance between the Structure Plan of BMRDA and the RMP of BDA and the fact that the plans of the BWSSB, BESCOM, BMTC and BDA "never talked to one another".
Anjali cited the example of Delhi Development Authority which had called for all line agency plans and consolidated them into the master plan. She also stressed the need to break down the Master Plan into local area plans as citizens could give inputs only at the local level.
Karveer of Kalyannagar Residents’ Association lamented that without a strict regulatory mechanism for implementing the zonal regulations and building bye-laws, etc., prescribed in the Plan, it would remain on paper and Bangalore would continue to develop in a haphazard way.
Dwarkanath of North Bangalore Residents’ Association questioned the very Constitutionality and legality of both BMRDA and BDA making plans for Bangalore when the 74th Constitutional Amendment required a Metropolitan Planning Committee with two-thirds elected representatives to make plans for the Bangalore Metropolitan Region and the local planning to be devolved to the urban local body, BBMP. Some others stressed the need to engage with the existing system while parallely working for the legal structures to be constituted.
The lack of a system for data-base management within BDA was highlighted by others. Vijayan Menon of the Koramangala Initaitive called on citizens’ groups to prepare a "vision document" for Bangalore within the framework of several national policies, such as the National Vendors’ Policy and the National Urban Transportation Policy, and push for its implementation by BDA through the BBMP.
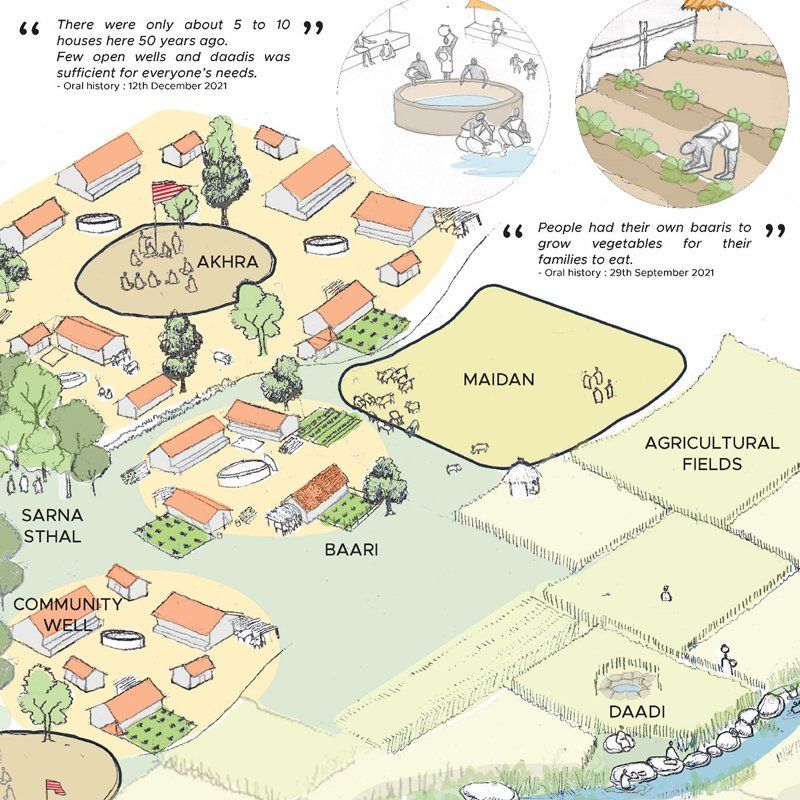
Being a member of the Adaptation Research Alliance, ARA (a global, collaborative effort to increase investment and opportunities for action research to develop/inform effective adaptation solutions) and an ARA Micro grantee, Integrated Design (INDÈ) was invited to organise a networking session at the Global Gobeshona Conference-2 (conference theme: exploring locally led adaptation and resilience for COP27). The networking session was titled ‘Situating Urban (City) Resilience within the City-Region’ and was held on 1 April 2022.

The online magazine SustainabilityNext carried an article by Benedict Paramanand titled “Has Fatigue Set into Civic Activism in Bengaluru?” The article caught my eye amidst the Covid 19 humdrum as I was looking for alternative news. I have been actively engaged in the debates around the (ill)growth and mis(management) of Bangalore for over two and half decades in my capacity as a professional planner straddling civic society, public policy circles and academia. The article revived in my mind some thoughts and suggestions that I articulate here. The attempt is not so much to answer the question, as it is to understand the shortcomings and limitations of civic activism in steering the complex politico-socio-economic and cultural layers that make up a vast conglomeration like Bengaluru. A disclaimer here merits mention. The premise that no individual stakeholder, public or private, has the knowledge and resources to tackle the wicked problems underpins successful governance arrangements. What this premise implies, by extension is that all stakeholders – public or private – have limitations. Civic Society (CS) is one amongst the numerous stakeholders that have a role – by no means a lesser one- to play. Yet, there are limitations to this role. While these limitations are embedded in the very nature of operation of the CS, there are conscious ways and means of overriding some limitations to move towards a larger impact. Bridging limitations is a critical need. Much of what I articulate while contextual to Bengaluru, perhaps holds true for civic activism across domains and geographies. To begin with, a critical question requiring reflection is the difference between civic activism and the much advocated (in (good) governance debates) Civic Society Organisation (CSO) engagement. These generally get clubbed in one category – while in theory and practice, that is not the case and therein lies the first limitation. Activism defined as direct vigorous action especially in support of or, in opposition to, one side of a controversial issue is willy-nilly an act of reaction. Reaction often leaves little space for taking distance and exploring the systemic cause of the challenge – the challenge itself sets the agenda. In contrast a proactive engagement of the civic society, through progressive partnerships while also triggered by a challenge is different in that the challenge is anticipated and therefore the agenda is set by civic society themselves. In Bengaluru, protests against the state-imposed flyover (# steelflyoverbeda ) and elevated corridors (# TenderRadduMadi ) is an example of the former. In contrast, the long-standing work on the ward committees which has seen some traction in the recent past – albeit slow and tardy – is an example of the latter. Having started as a proactive CSO engagement, the movement for neighbourhood planning and governance through ward committees (# NammaSamitiNamagaagi ) in the recent past has bordered on being reactionary, thereby hinging on activism. Although an ‘always proactive approach’ is not possible, given the capacity of our government to spring surprises, it is critical that the CS begins to move towards a proactive stance. There will always be a non-uniform interplay between being reactive and proactive. A second limitation, linked to the first, is the lack of capacity of the CS to act on relevant and practical evidence. This will require the CS to open their doors and develop progressive partnerships, including partnerships with policy makers, professionals (note that I do not use the word experts) and academia. An all-time reactionary mode of operation allows neither for collaborations nor evidence. Evidenced advocacy and conversations require domain knowledge (experienced domain knowledge is even better) which can facilitate knowledge production and mobilization. Activism hinges on passion (amongst other drivers) which is not the same as domain knowledge and knowledge mobilization. Both passion and domain knowledge have a role, yet the two can neither replace each other nor should be confused. Rather, passion that pivots on evidence and knowledge is a double-edged sword, one that has the capability to steer reactionary behavior to an informed proactive engagement. Such a move will serve to, over a period of time, course correct policies that are currently influenced by dominant political structures, electoral volatility and elite capture, as against being evidence based. A third limitation that needs consideration is the nature, purpose, goal and objective of the civic society coalition/group. Most often mobilisation is around a seemingly common purpose, goal and objective. For instance, groups that coalesced against large infrastructure projects as mentioned above or the demand for footpaths and public transit (# BusBhagyaBeku ) and sub-urban rail (# chukuBukuBeku ) are not homogeneous. It is often a mixed bag as against an imagined and perhaps desired integrated unit. Underpinning this pursuit of collective goals and objectives are individual desires, identities (which in themselves are multiple), beliefs, perspectives and previous experience, all of which are critical drivers, often leading to fragmented voices. This fragmentation notably, also derives from the inability to use evidence or domain knowledge. Elitist Activism Furthermore, activism in itself is and can be elitist. When linked to high levels of access it can be potentially hampered by what is referred to as ‘elite capture’. There are two types of activism: elite activism stemming from mobilization of charismatic individuals capable of getting their voice heard. Mass activism, in contrast, is where the general public, the haves and the have-nots, mobilize collectively. The two are not mutually exclusive, although both are critical. Barring a few occasions, Bengaluru’s activism has been elitist with a few voices that can access public policy corridors and therefore get heard. Consequently, consciously or unconsciously there is a leveraging of public policy for personal or limited gains (to a neighbourhood or a community). Activism is a luxury that not everyone can afford. Those who can afford it have a dual responsibility of using it to build bridges by roping in knowledge and experience on one hand and ensuring inclusion by creating spaces and opportunities for mass activism, on the other. The current modus operandi lacks on both counts. These shortcomings have led to what is being referred to as limited success, although limited from whose lens and success for whom is an additional enquiry, one that merits a separate post. What I do concur with is that at best the city has seen some cosmetic changes. Let me take the same two examples the article uses to demonstrate a going forward beyond cosmetic progress. First are the lakes in Bangalore that have seen a fair bit of activism. In many neighborhoods, thanks to the many charismatic residents, lakes have been claimed as better maintained natural resources. But for the initiatives of a few citizens, many lakes would have morphed into real estate projects. Yet, the same groups have done little to engage the larger neighborhoods to ensure that these natural resource ‘spaces’ become public ‘places’ for the neighborhood and the city. This would require a proactive engagement in identifying the larger neighborhood and the numerous linkages – backward and forward – that this neighborhood has had and can nurture with the lakes as public places. The second is the Tender Sure roads pioneered by Bengaluru. The implementation of Tender Sure roads is progressing incrementally moving from a pilot in the city core to radiating outwards in various directions. Putting aside the debates on the efficacy of the design as well as the appropriateness and relevance of the idea, the incremental implementation is marked by controversies on the criteria to shortlist roads such that both the visibility of and utility to the neighborhood and the city can be maximized. This too has not happened. Both these examples offer a critical insight: that the activism (and the few instances of engagement) has not translated into a thinking city. Changes are still hovering around the thinking individual. The transition to a thinking city is an emerging imperative, one that demands systemic change along various dimensions, some of which I have discussed above. To sum-up, sustained and big bang change as against cosmetic and incremental change is the need of the hour. It requires at the outset, one, more proactive engagement and less reactive activism; two, passion combined with experienced domain knowledge to trigger evidenced advocacy and change; and, three a less fragmented approach through creating meaningful spaces for mass activism along with the existing elite activism that the city has. While there may be numerous ways to act on these three, the Ward Committee space offer a ready platform for proactive action, evidence-based advocacy and wider participation. Arguably, this space is rife with political contestations and may seem a daunting challenge, yet, an engagement within this space is a surer foot forward. Clearly, there is a passion amongst Bangalore’s elite to be part of something bigger and this is a moment to be seized.


